Voltage
Voltage defined as the amount of potential energy between two points on a circuit. One point is more charged than the other. This difference between the two points is called voltage. It is measured in volt, which, technically, there is a potential energy difference between two points which will provide a joule of energy per coulomb of charge which passes through it. The name "Volt" is named after Italian physicist Alessandro Volta who invented the first chemical battery. The voltage is represented by the letters "V" in equations and schematic.
In a water tank analogy, the charge is represented by the amount of water, the voltage is represented by the pressure of the water, and the current is represented by the flow of water.
- Water = charge
- Pressure = voltage
- Flow = current
Consider the water tank at a certain height above the ground. There is a tube in the lower part of this tank. voltage can represent by the pressure at the end of the hose. The water in the tank represents the charge. The more water in the tank, the more charge, the more pressure is measured at the end of the tube.
By using the water analogy of water, we can see the voltage as the difference in height, which reduces the flow of water.
V = φ2 - φ1
V is the voltage between point 2 and 1 in volts (V).
The electric potential at point 2 is φ2 in volts (V).
The electric potential at point 1 is φ1 in volts (V).
In an electric circuit, the electric voltage is equal to the consumption of energy in Joules
divided by Electric charge.
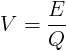
The voltage measured in V volts. E is the energy to be measured in J. Q is the electrical charge measured in the coulombs (C).
Voltage in series
The total voltage of several voltage sources or voltage drop in the series is their sum.
Vt = V1 + V2 + V3 + ...
Vt - Equivalent voltage source
V1 - voltage drop (V)
V2 - voltage drop (V)
V3 - voltage drop (V)
Voltage in parallel
In parallel the voltage source or voltage drop has equal voltage.
VT = V1 = V2 = V3 = ...
VT - Equivalent voltage source
V1 - voltage drop (V)
V2 -voltage drop (V)
V3 - voltage drop (V)
Voltage by country
The supply of AC voltage for each country may be different.






0 Comments